Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Some features of the histogram (hist) function#
In addition to the basic histogram, this demo shows a few optional features:
Setting the number of data bins.
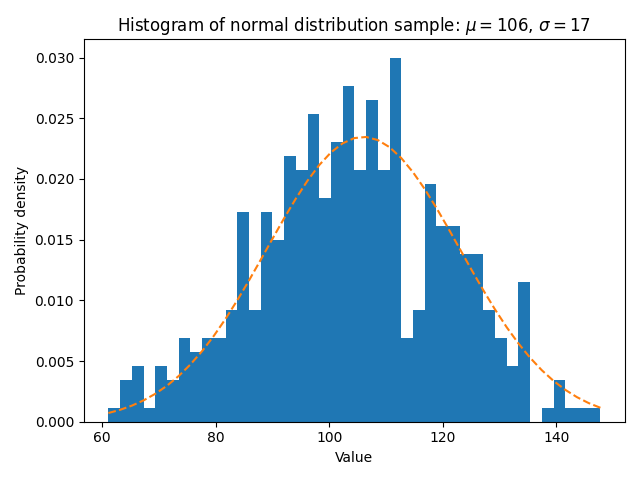
The density parameter, which normalizes bin heights so that the integral of the histogram is 1. The resulting histogram is an approximation of the probability density function.
Selecting different bin counts and sizes can significantly affect the shape of a histogram. The Astropy docs have a great section on how to select these parameters.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
rng = np.random.default_rng(19680801)
# example data
mu = 106 # mean of distribution
sigma = 17 # standard deviation of distribution
x = rng.normal(loc=mu, scale=sigma, size=420)
num_bins = 42
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# the histogram of the data
n, bins, patches = ax.hist(x, num_bins, density=True)
# add a 'best fit' line
y = ((1 / (np.sqrt(2 * np.pi) * sigma)) *
np.exp(-0.5 * (1 / sigma * (bins - mu))**2))
ax.plot(bins, y, '--')
ax.set_xlabel('Value')
ax.set_ylabel('Probability density')
ax.set_title('Histogram of normal distribution sample: '
fr'$\mu={mu:.0f}$, $\sigma={sigma:.0f}$')
# Tweak spacing to prevent clipping of ylabel
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
References
The use of the following functions, methods, classes and modules is shown in this example: