Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
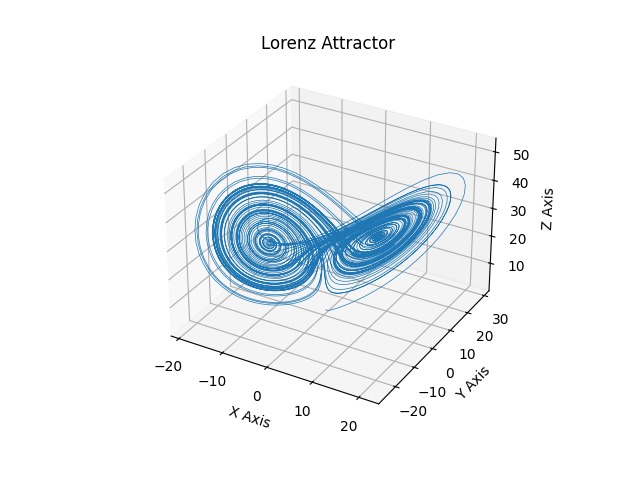
Lorenz attractor#
This is an example of plotting Edward Lorenz's 1963 "Deterministic Nonperiodic Flow" in a 3-dimensional space using mplot3d.
Note
Because this is a simple non-linear ODE, it would be more easily done using SciPy's ODE solver, but this approach depends only upon NumPy.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def lorenz(xyz, *, s=10, r=28, b=2.667):
"""
Parameters
----------
xyz : array-like, shape (3,)
Point of interest in three-dimensional space.
s, r, b : float
Parameters defining the Lorenz attractor.
Returns
-------
xyz_dot : array, shape (3,)
Values of the Lorenz attractor's partial derivatives at *xyz*.
"""
x, y, z = xyz
x_dot = s*(y - x)
y_dot = r*x - y - x*z
z_dot = x*y - b*z
return np.array([x_dot, y_dot, z_dot])
dt = 0.01
num_steps = 10000
xyzs = np.empty((num_steps + 1, 3)) # Need one more for the initial values
xyzs[0] = (0., 1., 1.05) # Set initial values
# Step through "time", calculating the partial derivatives at the current point
# and using them to estimate the next point
for i in range(num_steps):
xyzs[i + 1] = xyzs[i] + lorenz(xyzs[i]) * dt
# Plot
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(projection='3d')
ax.plot(*xyzs.T, lw=0.5)
ax.set_xlabel("X Axis")
ax.set_ylabel("Y Axis")
ax.set_zlabel("Z Axis")
ax.set_title("Lorenz Attractor")
plt.show()