Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Parasite axis demo#
This example demonstrates the use of parasite axis to plot multiple datasets onto one single plot.
Notice how in this example, par1 and par2 are both obtained by calling
twinx(), which ties their x-limits with the host's x-axis. From there, each
of those two axis behave separately from each other: different datasets can be
plotted, and the y-limits are adjusted separately.
This approach uses mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.parasite_axes.host_subplot and
mpl_toolkits.axisartist.axislines.Axes.
The standard and recommended approach is to use instead standard Matplotlib axes, as shown in the Multiple y-axis with Spines example.
An alternative approach using mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.parasite_axes.HostAxes
and mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.parasite_axes.ParasiteAxes is shown in the
Parasite Axes demo example.
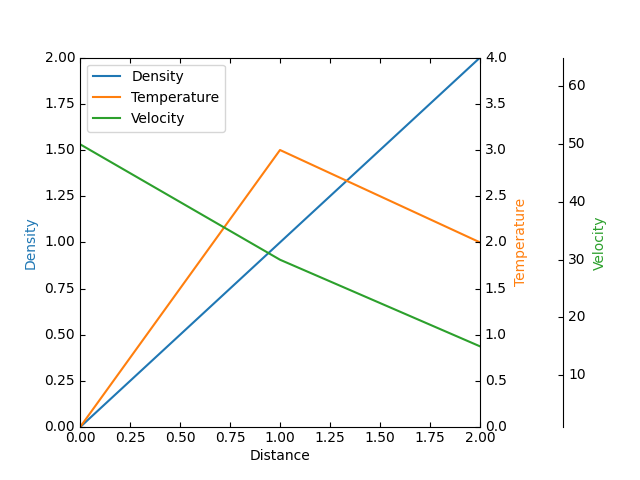
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits import axisartist
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import host_subplot
host = host_subplot(111, axes_class=axisartist.Axes)
plt.subplots_adjust(right=0.75)
par1 = host.twinx()
par2 = host.twinx()
par2.axis["right"] = par2.new_fixed_axis(loc="right", offset=(60, 0))
par1.axis["right"].toggle(all=True)
par2.axis["right"].toggle(all=True)
p1, = host.plot([0, 1, 2], [0, 1, 2], label="Density")
p2, = par1.plot([0, 1, 2], [0, 3, 2], label="Temperature")
p3, = par2.plot([0, 1, 2], [50, 30, 15], label="Velocity")
host.set(xlim=(0, 2), ylim=(0, 2), xlabel="Distance", ylabel="Density")
par1.set(ylim=(0, 4), ylabel="Temperature")
par2.set(ylim=(1, 65), ylabel="Velocity")
host.legend()
host.axis["left"].label.set_color(p1.get_color())
par1.axis["right"].label.set_color(p2.get_color())
par2.axis["right"].label.set_color(p3.get_color())
plt.show()