Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
3D surface with polar coordinates#
Demonstrates plotting a surface defined in polar coordinates. Uses the reversed version of the YlGnBu colormap. Also demonstrates writing axis labels with latex math mode.
Example contributed by Armin Moser.
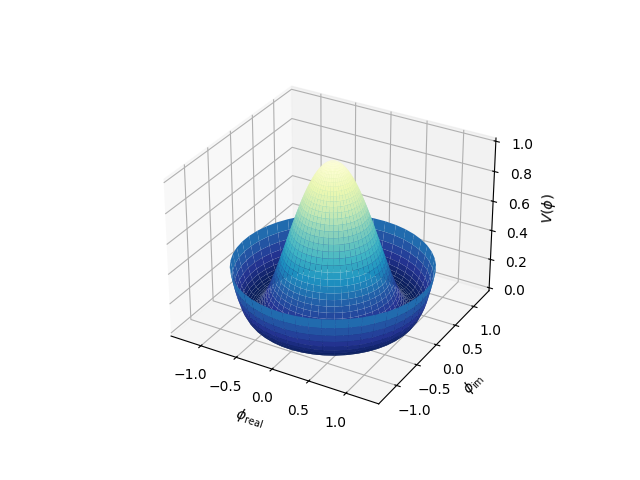
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(projection='3d')
# Create the mesh in polar coordinates and compute corresponding Z.
r = np.linspace(0, 1.25, 50)
p = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 50)
R, P = np.meshgrid(r, p)
Z = ((R**2 - 1)**2)
# Express the mesh in the cartesian system.
X, Y = R*np.cos(P), R*np.sin(P)
# Plot the surface.
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, cmap=plt.cm.YlGnBu_r)
# Tweak the limits and add latex math labels.
ax.set_zlim(0, 1)
ax.set_xlabel(r'$\phi_\mathrm{real}$')
ax.set_ylabel(r'$\phi_\mathrm{im}$')
ax.set_zlabel(r'$V(\phi)$')
plt.show()