matplotlib.axes.Axes.fill_between#
- Axes.fill_between(x, y1, y2=0, where=None, interpolate=False, step=None, *, data=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Fill the area between two horizontal curves.
The curves are defined by the points (x, y1) and (x, y2). This creates one or multiple polygons describing the filled area.
You may exclude some horizontal sections from filling using where.
By default, the edges connect the given points directly. Use step if the filling should be a step function, i.e. constant in between x.
- Parameters:
- xarray (length N)
The x coordinates of the nodes defining the curves.
- y1array (length N) or scalar
The y coordinates of the nodes defining the first curve.
- y2array (length N) or scalar, default: 0
The y coordinates of the nodes defining the second curve.
- wherearray of bool (length N), optional
Define where to exclude some horizontal regions from being filled. The filled regions are defined by the coordinates
x[where]. More precisely, fill betweenx[i]andx[i+1]ifwhere[i] and where[i+1]. Note that this definition implies that an isolated True value between two False values in where will not result in filling. Both sides of the True position remain unfilled due to the adjacent False values.- interpolatebool, default: False
This option is only relevant if where is used and the two curves are crossing each other.
Semantically, where is often used for y1 > y2 or similar. By default, the nodes of the polygon defining the filled region will only be placed at the positions in the x array. Such a polygon cannot describe the above semantics close to the intersection. The x-sections containing the intersection are simply clipped.
Setting interpolate to True will calculate the actual intersection point and extend the filled region up to this point.
- step{'pre', 'post', 'mid'}, optional
Define step if the filling should be a step function, i.e. constant in between x. The value determines where the step will occur:
'pre': The y value is continued constantly to the left from every x position, i.e. the interval
(x[i-1], x[i]]has the valuey[i].'post': The y value is continued constantly to the right from every x position, i.e. the interval
[x[i], x[i+1])has the valuey[i].'mid': Steps occur half-way between the x positions.
- Returns:
PolyCollectionA
PolyCollectioncontaining the plotted polygons.
- Other Parameters:
- dataindexable object, optional
If given, the following parameters also accept a string
s, which is interpreted asdata[s](unless this raises an exception):x, y1, y2, where
- **kwargs
All other keyword arguments are passed on to
PolyCollection. They control thePolygonproperties:Property
Description
a filter function, which takes a (m, n, 3) float array and a dpi value, and returns a (m, n, 3) array and two offsets from the bottom left corner of the image
array-like or scalar or None
bool
antialiasedor aa or antialiasedsbool or list of bools
array-like or None
CapStyleor {'butt', 'projecting', 'round'}(vmin: float, vmax: float)
BboxBaseor Nonebool
Patch or (Path, Transform) or None
Colormapor str or Nonecolor or list of RGBA tuples
edgecoloror ec or edgecolorscolor or list of colors or 'face'
facecoloror facecolors or fccolor or list of colors
str
{'/', '\', '|', '-', '+', 'x', 'o', 'O', '.', '*'}
bool
JoinStyleor {'miter', 'round', 'bevel'}object
linestyleor dashes or linestyles or lsstr or tuple or list thereof
linewidthor linewidths or lwfloat or list of floats
bool
Normalizeor str or Noneoffset_transformor transOffset(N, 2) or (2,) array-like
list of
AbstractPathEffectlist of array-like
None or bool or float or callable
float
bool
sizesnumpy.ndarrayor None(scale: float, length: float, randomness: float)
bool or None
str
list of str or None
list of array-like
unknown
bool
float
See also
fill_betweenFill between two sets of y-values.
fill_betweenxFill between two sets of x-values.
Examples using matplotlib.axes.Axes.fill_between#
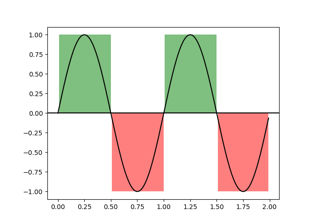
Shade regions defined by a logical mask using fill_between