numpy.random.poisson¶
-
numpy.random.poisson(lam=1.0, size=None)¶ Draw samples from a Poisson distribution.
The Poisson distribution is the limit of the binomial distribution for large N.
Note
New code should use the
poissonmethod of adefault_rng()instance instead; see random-quick-start.- Parameters
- lamfloat or array_like of floats
Expectation of interval, must be >= 0. A sequence of expectation intervals must be broadcastable over the requested size.
- sizeint or tuple of ints, optional
Output shape. If the given shape is, e.g.,
(m, n, k), thenm * n * ksamples are drawn. If size isNone(default), a single value is returned iflamis a scalar. Otherwise,np.array(lam).sizesamples are drawn.
- Returns
- outndarray or scalar
Drawn samples from the parameterized Poisson distribution.
See also
Generator.poissonwhich should be used for new code.
Notes
The Poisson distribution
For events with an expected separation
the Poisson distribution
describes the probability of
events occurring within the observed interval
.
Because the output is limited to the range of the C int64 type, a ValueError is raised when lam is within 10 sigma of the maximum representable value.
References
- 1
Weisstein, Eric W. “Poisson Distribution.” From MathWorld–A Wolfram Web Resource. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/PoissonDistribution.html
- 2
Wikipedia, “Poisson distribution”, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Poisson_distribution
Examples
Draw samples from the distribution:
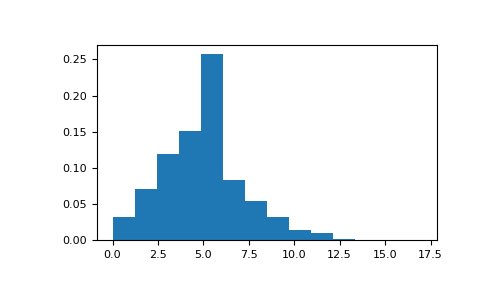
>>> import numpy as np >>> s = np.random.poisson(5, 10000)
Display histogram of the sample:
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s, 14, density=True) >>> plt.show()
Draw each 100 values for lambda 100 and 500:
>>> s = np.random.poisson(lam=(100., 500.), size=(100, 2))
